The modern office floor is a marvel of efficiency, with machines whirring in perfect harmony. But behind this automation symphony is a hidden driver: the embedded system for industrial automation. These microcomputers are the brains behind the brain, embedded in robots, assembly lines and control systems. They acquire data from sensors, make real-time decisions and control actuators to execute complex tasks flawlessly.
Choosing the right embedded system hardware design and configuration is critical for industrial automation. It’s the difference between a smooth, efficient operation and one plagued by costly delays, errors and downtime. In this blog, we will explore the top factors to consider when choosing the right embedded system for industrial automation and control.
 Key Considerations in embedded systems :
Key Considerations in embedded systems :
1. Power Processing and Memory
The heart of any embedded systems for industrial automation is its processing power and memory capacity. Just as your computer needs a large amount of muscle to run complex software, the system you choose must be able to handle your complex technical applications.
This means two main things, data processing and real-time processing are memory-based. The system requires sufficient memory to store program instructions, process incoming sensor data, and generate control signals. For example, a system that manages basic machine parameters may require less memory compared to one that uses advanced machine learning algorithms to cover the storage processes By carefully considering data processing and real-time control application requirements, you can choose an embedded system that balances processing power and memory capacity This ensures efficiency and avoids performance bottlenecks that can hamper your industrial automation applications approach.
2. Real-time Performance in Embedded Systems for Industrial Automation:
In industrial automation, timing is everything. Many products rely on deterministic operation, which means that the system must guarantee a certain response time for critical tasks. For example, in conveyor belt control, a missed timer can result in product degradation or even a safety hazard. Several factors affect real-time performance:
Hardware: A powerful processor with low latency (latency) is required. Specialized real-time activation systems can dramatically improve responsiveness.
Software Architecture: Efficient code optimization and reduction of unnecessary background tasks ensure that the system prioritizes critical real-time functions.
3. Communication and Communication Policy:
Embedded systems don’t work in isolation. They must communicate with other devices and operating systems to exchange data and run programs. This requires compatibility with established technical networks. Some common examples are:
Modbus: A widely used protocol for seamless communication between devices.
PROFIBUS: A high-speed protocol for complex industrial automation systems.
Choosing an embedded system that supports the right protocols ensures seamless integration into your existing industrial network.
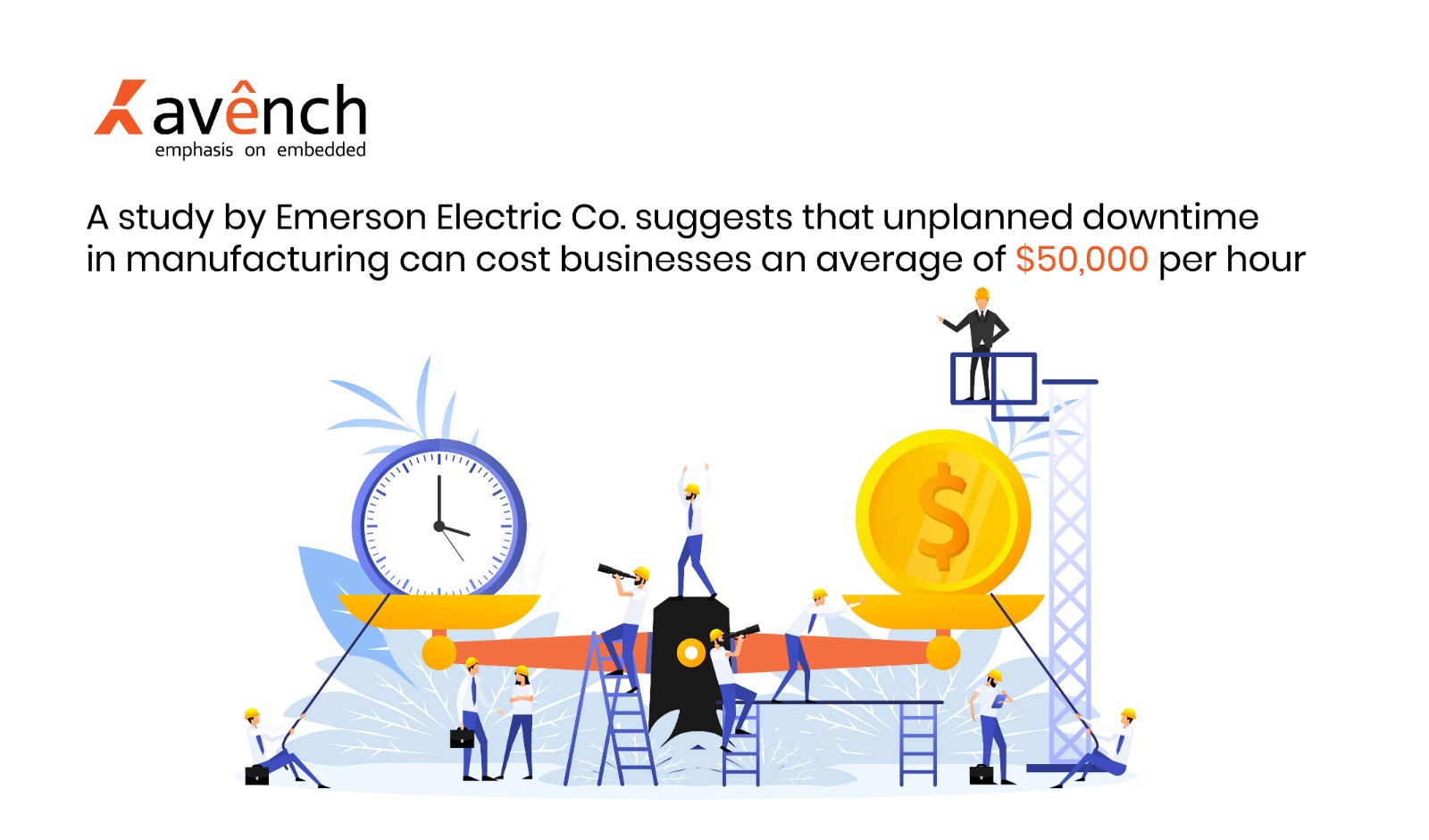
4. Trust & Security:
Timing is key in engineering. A system failure can lead to a halt in production and a significant loss of revenue. This is why reliability and security are important considerations. Implementing robust security measures in embedded systems is crucial. Look for factors that increase system efficiency, e.g.
Redundancy: Having backup components (e.g., processors and power supplies) keeps you running even if one element fails.
Error correction: Methods of identifying and correcting errors in data transmission and processing reduce interruptions.
5. Environmental Conditions:
The technical environment can be harsh. Installed systems must withstand extreme temperatures, vibration, dust and even water. Here’s what to consider:
Hardware Components: Displays components that are sealed for expected environmental conditions. Industrial-grade processors and memory modules provide excellent durability.
Environment: The physical enclosure of the system must protect the components inside from dust, moisture and physical impacts. Consider enclosed rooms with fresh air for heat transfer.
6. Development Tools and Software Support:
The development of turnkey software development requires efficient control programs for embedded systems and requires special tools and software libraries. Look for manufacturers that offer readily available development tools and well-documented libraries specific to their hardware. Also, consider the number of animals available to the manufacturers. Reliable technical support can be invaluable in troubleshooting and ensuring compatibility with future software updates.
7. Cost and Flexibility in Embedded Systems for Industrial Automation:
It is important to find the right balance between cost and efficiency. Higher-order settings may be too much for simple applications. However, consider future expansion needs. Choose an embedded system with some level of scalability to accommodate potential improvements to your industrial automation system.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right embedded systems for your industrial automation needs requires careful consideration of a variety of factors. By prioritizing the key considerations outlined above, you can ensure efficiency, reliability, and seamless integration with your existing system. Remember that the best-embedded system is an investment that optimizes your industrial automation processes, increasing efficiency, productivity and cost savings in the long run.
Avench is one of the leading embedded product design companies in usa. For any sales queries, contact us at +1 (775) 404-5757. You can also email us at sales@avench.com. We will be happy to assist you.